The skin is the largest organ in our body, and your skin type may be more unique than you think. Skin type determines your sensitivity to sunlight, and sunlight affects your skin color.
All cosmetic laser treatments are actually the use of photoelectric technology to stimulate the skin and activate the body’s regeneration mechanism. Among them, skin color has a huge impact on the parameters of laser treatment, because people with different skin colors have different tolerances to photothermal effects. Therefore, if you want to learn the core technology of photoelectric cosmetic lasers, the first lesson is to familiarize yourself with the skin type and structure of the human body.

In this article, we will learn about all the skin types of humans and know how to distinguish and know which type your skin color belongs to.
Optical properties of skin tissue.
Skin color is largely determined by the properties of the epidermis, which acts as a biological filter. Visible light incident on the skin can be transmitted, absorbed, scattered or reflected in different proportions. The color perceived by the human eye is the result of these phenomena and is determined by chromophores such as melanin in keratinocytes, carotene in dermal capillaries and the presence of hemoglobin.
A small part of the incident light beam on the skin surface is directly reflected by the interface formed by the skin stratum corneum and the outer air, while most of the incident light is refracted by the skin surface and enters the epidermis and dermis in turn, and after being scattered and absorbed, it will return to the skin surface and enter the air, forming diffuse reflected light.
Basically, the skin color observed by the eyes is mainly determined by the smoothness, light transmittance, reflectivity, etc. of the skin tissue.

What are the types of human skin colors?
Skin type is a way of classifying skin based on how it reacts to UV radiation. The most widely accepted skin type classification is the Fitzpatrick classification, which is based on how easily the skin burns and how well it tans. It divides skin color into six categories based on how sensitive people are to sunlight:
- Type I skin color: snow-white skin color, very easy to sunburn, can’t get tan at all. This skin type needs the highest level of sun protection.
- Type II skin color: fair skin color, also easy to sunburn, difficult to tan. This skin type needs to choose sunscreen products with a high protection index.
- Type III skin color: light brown-white skin, easy to sunburn, can get a slight tan.
- Type IV skin color: medium skin color, not easy to sunburn, can get a significant tan. This skin type has slightly lower sun protection requirements.
- Type V skin color: dark brown skin color, difficult to sunburn, can get a dark and bright natural skin color.
- Type VI skin color: dark black skin color, basically no sunburn, the darkest skin color.

In addition to estimating the initial UV dose, determining your skin type can help us predict skin damage and avoid the risk of skin cancer. Our skin color is determined by melanin produced by melanocytes, which absorbs and scatters UV rays to protect the skin from damage. Therefore, people with darker skin tend to be more resistant to UV rays, while people with lighter skin are more susceptible to UV damage.
What are the main factors that affect skin color?
Normal skin color is determined by the content of melanin, carotene, oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin in the skin, and is also closely related to many factors such as the thickness and water content of the stratum corneum, blood flow, and oxygen content in the blood.
- Melanin is the most important pigment that determines the color of human skin. It is synthesized in melanocytes located in the basal layer of the epidermis, and then transmitted to the adjacent keratinocytes through the dendrites of melanocytes, and moves to the upper layer of the epidermis with keratinocytes, thus affecting the skin color.
- Carotene is a carotenoid pigment that can only be ingested through food. Carotene in the blood is easily deposited in the stratum corneum, and produces a distinct yellow color in areas with thick stratum corneum and subcutaneous tissue. Women’s skin often has more carotene than men.
- Hemoglobin exists in red blood cells and can combine with oxygen molecules (called “oxyhemoglobin”) to transport oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. Oxyhemoglobin exists in arterial blood and makes the blood bright red. Hemoglobin after deoxygenation is called “deoxyhemoglobin”, which makes the blood appear dark red in venous blood. The color of blood can affect the skin color of capillary-rich areas such as cheeks.
- When the stratum corneum is thinner and contains more water, the skin has better transparency and can transmit more blood color, making the skin appear red; on the contrary, when the stratum corneum is thicker and contains less water, the skin has lower transparency and appears yellow.
Among the different races, the biggest difference is in skin color, which can be roughly divided into three races: white, yellow and black.
- The melanin content in the epidermis of Caucasian skin is very low, the skin is very transparent, the oxygenated hemoglobin content is high, and the skin appears pink.
- The skin of black people contains more melanin, and the hemoglobin content in the blood is lower.
- The melanin in the skin of yellow people has a stronger ability to absorb ultraviolet rays.
- At the same time, the pigment of male skin is often richer than that of female skin; the pigment of the elderly skin is richer than that of the young; the palms and heels have less pigment, while the genitals, nipples and other parts have more pigment.
In addition to congenital reasons, some people’s skin color is greatly affected by acquired factors. Ultraviolet rays are stronger in summer, and direct exposure can cause melanin deposition and be difficult to metabolize. Even people with naturally fair skin can have uneven pigmentation.

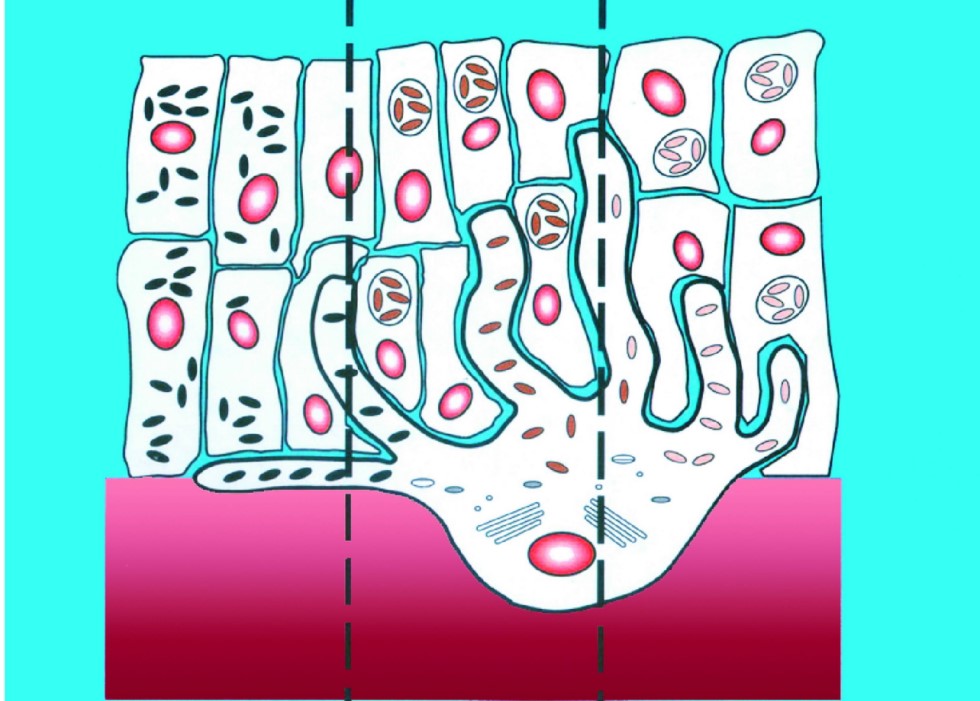
Melanin is synthesized by melanocytes located in the basal layer. Melanocytes differentiate from the neural crest and are located in the skin, eyes, and central nervous system in the early embryo.
The following three aspects are the main mechanisms by which melanin determines skin color.
1. Constitutive skin color and variable skin color.
Skin color determined by melanin is divided into constitutive skin color and facultative skin color.
Constitutive skin color is the skin color determined by genes without the influence of sunlight and other factors, such as the skin on the buttocks and inner upper arms.
Facultative skin color, also known as inducible skin color, is the skin color that deepens due to the increase of melanin caused by various endogenous (such as endocrine and paracrine changes) or exogenous (such as sun exposure) factors.
2. Skin color differences between different races.
Skin color, which is determined by melanin, is directly related to different races. The activity of melanocytes in the skin varies between different races, and the number and structure of melanosomes are different. The world’s races are usually divided into three major races, namely yellow race (Asians), white race (Caucasians and Nordic people) and black race (Africans and African Americans). Some people also advocate the division of brown race (Australians).
Studies have found that the number of melanocytes in the skin is almost the same between different races or genders. However, the ability of melanocytes to synthesize melanin (i.e., the activity of melanocytes) varies significantly between different races and is easily affected by factors such as sun exposure. Melanocyte activity is specifically reflected in the number and size of pigmented melanosomes produced, as well as the efficiency of transport to keratinocytes.
Melanosomes in Caucasian skin exist only in small amounts in the basal cells, with only stage I, II, and III melanosomes, but no stage IV melanosomes; in the epidermis of yellow people, there are stage II, III, and IV melanosomes; in black people, there are stage IV melanosomes, and these melanosomes are distributed in cells of all layers of the epidermis.
Note: Stage IV melanosomes are mature melanin and are black. Stage I, II, and III melanosomes are immature melanosomes and are not black.
Studies have found that in black skin, melanocytes contain more than 200 melanosomes. The diameter of the melanosomes is 0.5-0.8mm and there is no membrane. Melanosomes in white skin contain less than 20 melanosomes. The diameter of the melanosomes is 0.3-0.5mm and they are clustered in the membrane[6]. Melanosomes in light skin degrade faster than those in dark skin.
So, it is not only the maturity of the melanosomes, but also the number of melanosomes that plays an important role in the depth of skin color.
Dark-skinned blacks or African Americans have larger melanosomes that are usually dispersed. Light-skinned Europeans and Americans have smaller melanosomes that are clustered in the limiting membrane. Intermediate skin tones, such as yellow or brown skin in Asians, contain both large, dispersed melanosomes and small, clustered melanosomes.
3. The effects of eumelanin and pheomelanin on skin color.
It is generally believed that genetics determines the levels of eumelanin and pheomelanin. Most melanin in the skin, hair, and eyes is a mixture of eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is brown-black, while pheomelanin is yellow-red. Light-colored melanocytes contain more pheomelanin than dark-colored melanocytes[6]. Studies have found that Caucasians have the lowest eumelanin levels, Asians have higher eumelanin levels, and African Americans have the highest eumelanin levels.
4. The impact of carotene on skin color.
Under normal circumstances, carotene has little effect on skin color. However, for those who often eat foods rich in carotene, such as citrus fruits and pumpkins, the amount of carotene in the blood will increase significantly. A large amount of carotene will cause the skin and sclera to turn yellow, a condition called “carotenemia”. If the hands, feet and face are obviously yellow, “carotenemia” should be considered first.
Objective test methods for skin color.
Skin color is mainly determined by pigments such as melanin, hemoglobin, and carotene. Different pigments lead to different skin colors.
Skin color can be defined using the CIE L*a*b* color space. The L value represents brightness, with values ranging from 0 to 100, representing from black to white. The a value represents redness, with values ranging from positive to negative, representing from red to green. The b value represents yellowness, with values ranging from positive to negative, representing from yellow to blue.
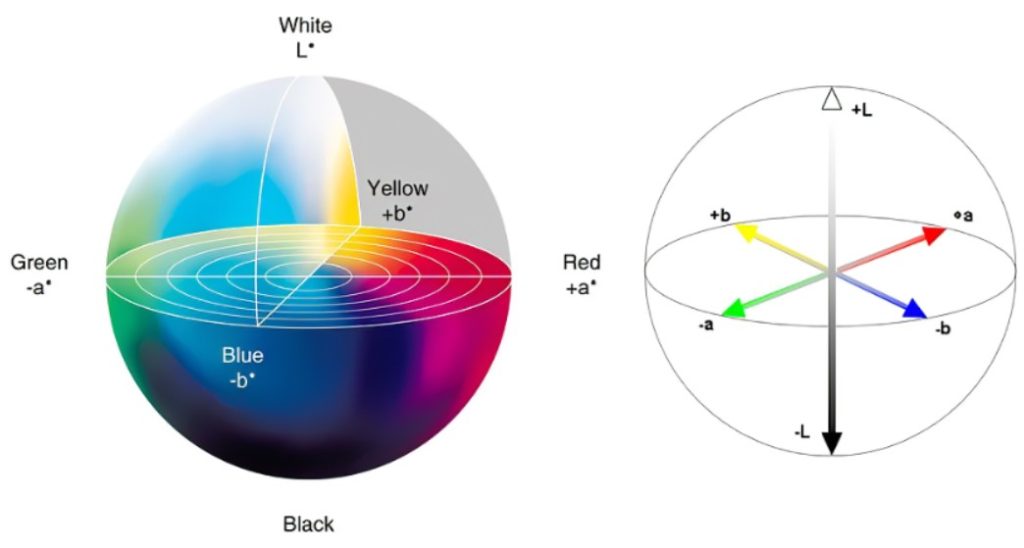
ITA° can be obtained through L* and b* parameters to evaluate the skin color depth. The larger the ITA, the lighter the skin color.
ITA° classification of skin color: very light skin > 55° > light skin > 41° > medium skin > 28° > tanned skin > 10° > tan skin > -30° > black skin.
Currently, there are mainly two types of methods for testing skin color. One is a test instrument based on the skin reflection light spectrum, and the other is based on skin imaging and analysis.
How to identify your skin type?
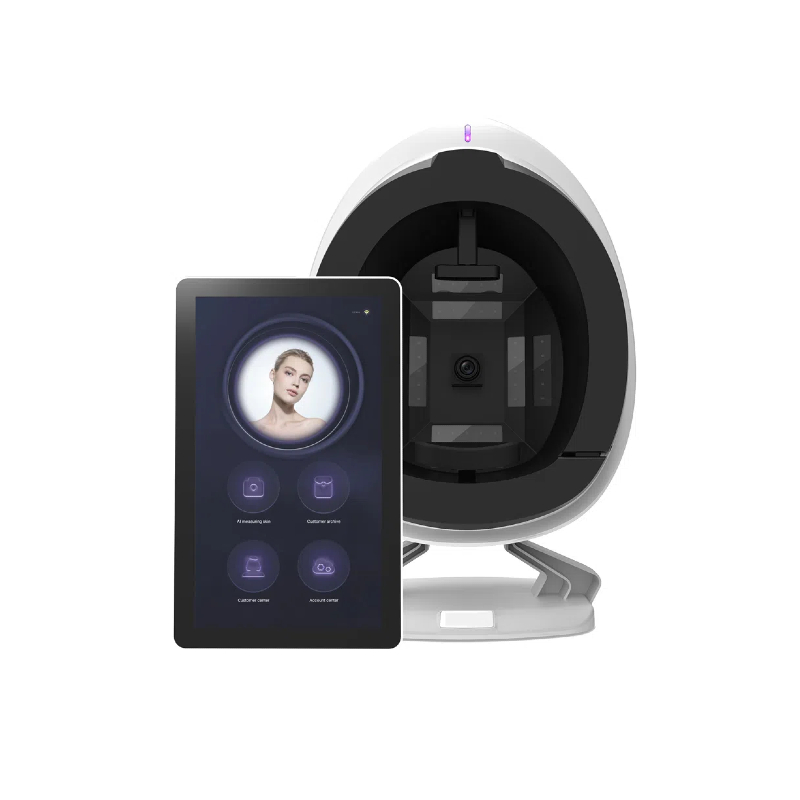
There are many ways to judge skin color. We can make simple judgments by race, skin color code, etc. But if you need to accurately judge your skin condition, including skin color and skin type, you can use a professional skin analyzer!
LitonLaser produces a professional skin analyzer. By using it to take pictures, the ultra-high pixels will fully preserve your skin condition. Through the cloud AI big data for detailed comparison, you can get your skin condition report, which can get your skin type and other skin information.

Summary of Skin Color Types.
- Skin color is mainly composed of four biological pigments in the skin: melanin, oxygenated hemoglobin, reduced hemoglobin and carotene.
- Blood circulation, thickening of the stratum corneum and aging of the dermis are also important factors affecting skin color (introduced in the next issue).
- Skin color determined by melanin is divided into constitutive skin color and variable skin color.
- Skin color determined by melanin is directly related to different races. The activity of melanocytes in the skin of different races is different, and the number and structure of melanosomes are different.
- People with dark skin have larger melanosomes and are dispersed. People with light skin have smaller melanosomes and are aggregated in the limiting membrane. The yellow skin of Asians contains both large and dispersed melanosomes and small and aggregated melanosomes.
- Light melanocytes contain more pheomelanin than dark melanocytes. The darker the skin color, the higher the content of eumelanin.
- If you need to quickly determine the skin type and condition, you can use the VISIA skin analyzer from LitonLaser beauty equipment manufacturer.
FAQs about skin color index and types.
Q: What is my skin type?
A: Skin type includes multi-dimensional information such as skin color, skin condition, skin problems, etc. We need to judge the specific skin condition before we can continue beauty treatment and improvement.
Q: What type of skin color do I have?
A: You can simply determine which type of skin color you have by race and color code, or you can use a skin analyzer to test the skin condition and all information and get the exact skin type.
Q: What are the skin color types?
A: Skin type is a way to classify skin based on how it responds to UV rays. The most widely accepted skin type classification is the Fitzpatrick classification, which is based on how easily the skin burns and how well it tans. It divides skin color into six categories, from I to VI, based on how sensitive people are to sunlight.